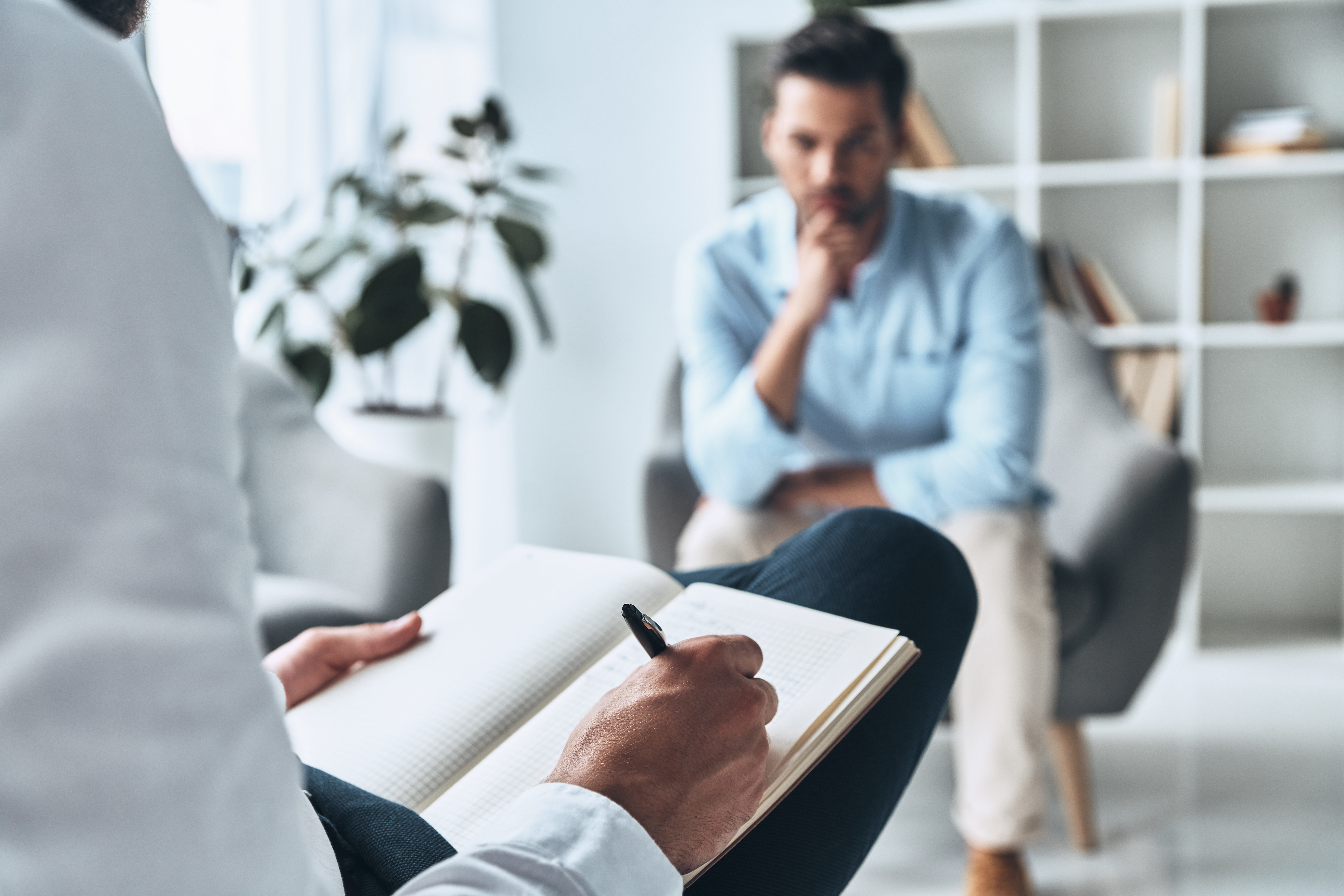
7 Types of ADHD
Classic ADHD
This type of ADHD also may be evident at an early age – even as a baby. In children it shows up in a restless, noisy, talkative, impulsive, and demanding nature. Symptoms of classic ADHD include inattentiveness, easy distraction, disorganization, impulsiveness, poor listening, carelessness, forgetfulness, restlessness (constant fidgeting), noisiness, constant talking.
Inattentive ADHD
The second most common type of ADHD, this version seems almost an inverse of classic ADHD, as sufferers are usually quiet, introverted, and daydream. However, it is often missed in diagnoses because the children that have it do not require constant attention. Symptoms of inattentive ADHD include trouble focusing, easy distraction, disorganization, poor listening, tendency to lose things, carelessness, forgetfulness, excessive daydreaming, boredom, apathy.
Overfocused ADD
Instead of jumping around and being unable to focus on one thing, people with overfocused ADHD can only focus on one thing – at the expense of everything else in their lives. This includes focusing exclusively on negative thought patterns and behaviors. This type of ADHD is common amongst substance abusers and symptoms include most of the core symptoms of classic ADHD – although they may or not may not be hyperactive. Other signs include excessive or senseless worrying, argumentativeness, compulsive behavior, inflexibility, tendency to hold grudges, and a need for control.
Temporal Lobe ADHD
As this effects the brain’s temporal lobe, people with this type of ADHD have classic ADHD symptoms, along with problems in learning, memory, mood instability, aggression, and temper (even violence). It can even result from head injuries. Aside from classic symptoms, signs of temporal lobe ADHD include memory problems, auditory processing issues, irritability, quick temper, spaciness or confusion, baseless panic and/or fear, visual changes (seeing shadows or objects changing shape), déjà vu, sensitivity or mild paranoia, headaches or abdominal pain of uncertain origin, dark thoughts (even suicidal or homicidal) and learning disabilities.
Limbic ADHD
The limbic area of the brain/brain stem controls your emotions. Therefore, those with limbic ADHD may experience continued and intense emotional sensations – including depression, so it must be thoroughly explored to determine if depression is caused by ADHD or is a separate issue. Apart from the classic symptoms of ADHD, limbic ADHD includes moodiness, negativity, low energy, frequent irritability, tendency for social isolation, hopelessness and helplessness, feelings of guilt, sleep changes, and low self-esteem.
Ring of Fire ADHD
This type of ADHD sees high activity occurring throughout the brain. This can lead to the sufferer feeling overwhelmed with thoughts and emotions that never end. Ring of fire ADHD may sometimes be the result of an allergic reaction, infection, or inflammation in the brain. It can also be related to bipolar disorder and studies show that many who suffer from ring of fire ADHD also suffer from bipolar disorder. Symptoms of ring of fire ADHD include classic attention deficit symptoms, as well as sensitivity to noise, light, or touch, patterned moodiness, inflexibility, hostility, selfishness, unpredictable behavior, periods of impulsiveness, fast talking, racing thoughts, and irritability.
Anxious ADHD
This particular mental disorder means that the part of your brain (the basal ganglia, located right at the center of the brain, near the base) that determines your resting emotional/physical state is overstimulated. This generally results in an anxious or nervous disposition. Along with core symptoms of ADHD, sufferers of anxious ADHD may also display physical stress symptoms (headaches, stomach pain, jaw pain), not know how to react in social settings, be excessively nervous about public speaking, be an eternal pessimist, avoid conflict, and have an irrational fear of being judged.